trade carbon credits
If you are interested in participating in a voluntary carbon market, it is important to understand how it works. The process is similar to a compliance market, but with a voluntary twist.
In a compliance trade carbon credits market, an organization is given a certain number of carbon credits to offset its emissions. If the organization exceeds the cap, it must purchase additional credits from another company. The cap on emissions is set by the government. The cap decreases over time. The cap is usually a percentage of the company’s total emissions. However, the cap on emissions can vary from state to state.
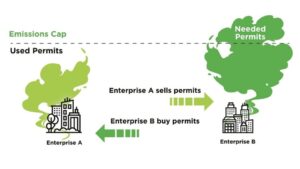
The number of carbon credits issued annually is based on the emission thresholds set by the government. The number of credits is also dependent on the attributes associated with the underlying project. These attributes can be determined by a third party auditor. These attributes vary in value, and the price of each credit is different from market to market.
can you trade carbon credits
One of the earliest carbon markets was created in the 1997 Kyoto Protocol. Since then, many international markets have emerged. In addition, states have launched regional greenhouse gas programs. Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Maryland, Rhode Island, and Delaware have all launched their own voluntary greenhouse gas initiatives.
The United Nations Clean Development Mechanism, created from the Kyoto Protocol, is the most active compliance carbon offset program. It is designed to help countries meet their commitments to reduce their carbon dioxide output. Ultimately, a global market is needed to mitigate the effects of climate change.
The most common form of offset occurs when an organization purchases the right to release its emissions. Companies that produce more emissions than they are allotted can purchase carbon offsets from other companies that have reduced their CO2 production. A company can also sell its excess credits on the market.
There are also other forms of carbon credits. These include Gold Carbon credits, which are tradable certificates that allow non-governmental organizations to earn money while reducing their emissions. The US has its own carbon market, namely the Californian Carbon Market.
Carbon trading, or “cap and trade” programs, are a way to reduce global carbon dioxide emissions. They are a market where companies can buy and sell rights to emit a certain amount of CO2. These permits are in digital format and are held in electronic “registry” accounts. They are eventually made available to end users when they are needed for regulatory compliance obligations.
As the climate crisis continues to progress, it is increasingly important that we find ways to offset our carbon emissions. As more people become aware of the negative impact of climate change, companies are turning to carbon markets to offset their emissions. In fact, the rising demand for such products has prompted a surge of investment in carbon markets around the world.
Choosing a company to sell carbon credits is a complex decision. You need to know the regulations, prices, and attributes of the specific market you are looking to enter.